18554493114
Call us for any question.
- support@aigrowth-solutions.com
- 349 Blue Point Rd Farmingville, NY 11738,USA
Call us for any question.
18554493114
Search for products
Blog Detail
- Home
- Blog
- Details
How Does Data Recovery Differ for Hard Drives Vs. SSDS?
In the digital age, data is the backbone of both business and personal operations. From important business documents to precious personal memories, data loss can be devastating. However, the process of retrieving lost data is not always straightforward. How data recovery works can vary depending on the type of storage device you use. In this post, we will dive into the differences between recovering data from traditional hard drives (HDDs) and solid-state drives (SSDs). Understanding how these devices function and fail can provide insight into the challenges and solutions when it comes to Data Recovery Services.
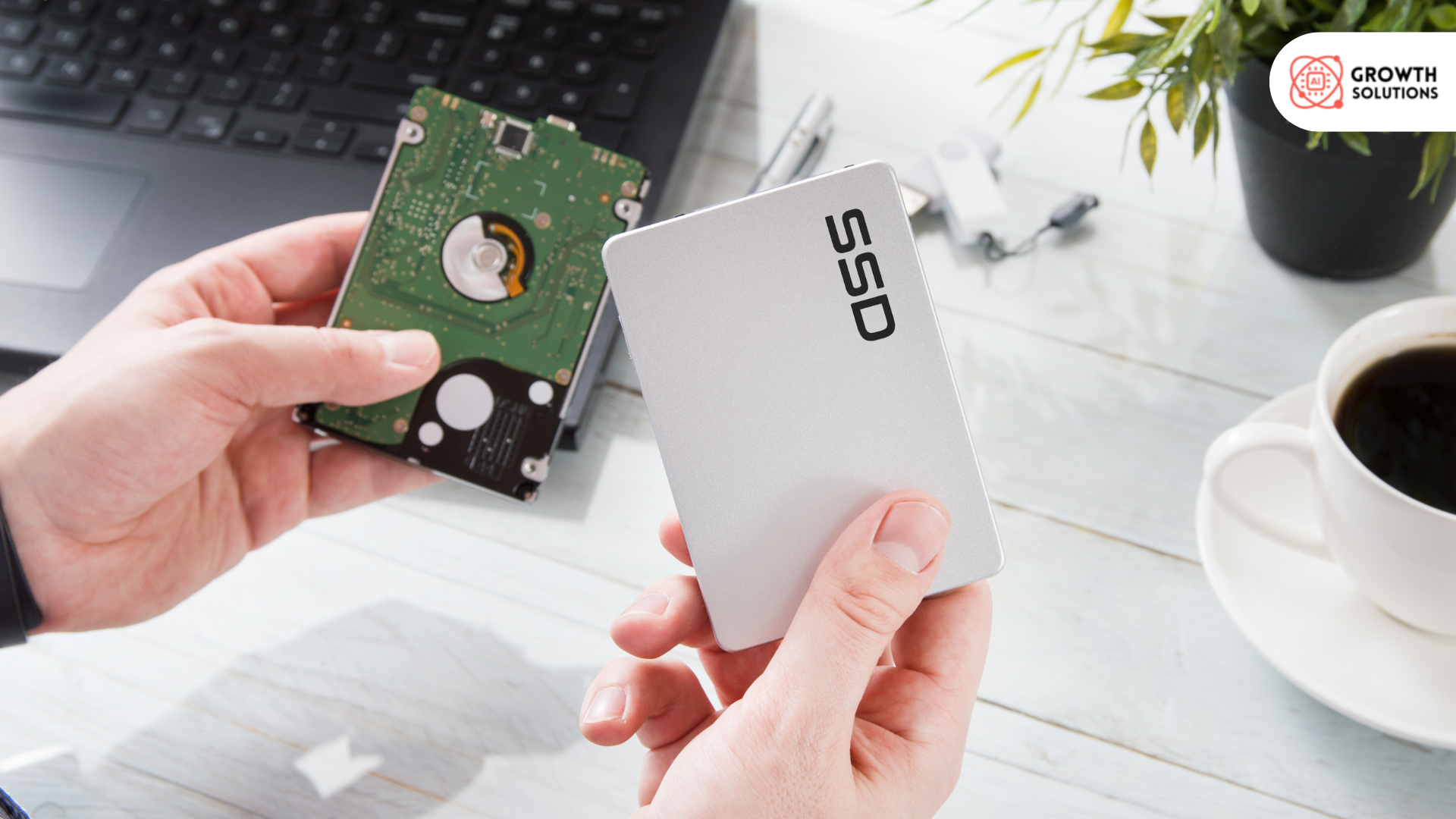
What is a Hard Drive and How Does It Store Data?
Traditional hard drives, or HDDs, use magnetic storage to read and write data. Inside the hard drive, spinning platters are coated with a magnetic material, and a read/write head moves over the platters to access or write data. The physical spinning of the platters allows for data retrieval but also makes hard drives prone to physical damage. If the hard drive is dropped or suffers any mechanical failure, the data could be compromised. These physical elements make hard drives more vulnerable to damage compared to their newer counterparts, like SSDs.
When it comes to data recovery, recovering data from an HDD usually involves accessing the physical components of the hard drive. If the drive has suffered physical damage, skilled technicians can attempt to repair it in a cleanroom environment to recover the data. On the other hand, if the damage is logical, meaning no physical harm has been done, software tools are used to scan the hard drive for lost or corrupted files.
What is an SSD and How Does It Differ From a Hard Drive?
Unlike HDDs, SSDs don’t rely on physical moving parts. Instead, they store data using flash memory chips, which retain data even when power is lost. This makes SSDs faster and more durable compared to traditional hard drives. The speed of SSDs is a significant improvement over HDDs, as they provide quicker boot-up times, faster file transfers, and less mechanical failure.
However, SSDs come with their own unique challenges when it comes to data recovery. The lack of moving parts means that physical damage is less of an issue, but SSDs have a limited number of write cycles. This can make the data recovery process more complicated when issues such as power failure, firmware corruption, or faulty controllers occur. Additionally, SSDs use technologies like wear leveling and TRIM, which are designed to optimize performance and prolong the life of the drive. These technologies, while beneficial for regular use, can make data recovery much more difficult once data is erased or corrupted.
Data Recovery for Hard Drives: Common Methods
Recovering data from an HDD often involves a variety of methods depending on the type of failure. If the failure is mechanical, such as a head crash or motor failure, Data Recovery Services typically involve opening the drive in a cleanroom to replace faulty components, like the heads or platters, in an effort to retrieve the data.
For logical failures, where the data is still intact but inaccessible due to corruption, partition issues, or accidental deletion, data recovery technicians use specialized software to rebuild the file system and recover the lost data. With the right tools, skilled technicians can often recover files even from drives with corrupted partitions or formatted disks. However, the recovery process for an HDD may be slower than an SSD and comes with a higher risk of permanent data loss if not done correctly.
Data Recovery for SSDs: How It’s Different from Hard Drives
SSDs present a unique set of challenges for Data Recovery Services. Since SSDs don’t use mechanical components, they are less prone to physical damage than HDDs, but the data recovery process can be more complicated due to the technology they use. One of the main issues is TRIM, a command that helps the SSD clean up unused data blocks to improve performance. While TRIM is useful for maintaining the longevity and performance of an SSD, it also permanently erases deleted data, making it harder to recover once the data is overwritten.
Another challenge is wear leveling, which distributes data evenly across the memory cells of the SSD to prevent overuse of any particular area. While this helps prolong the life of the drive, it can make it more difficult for Data Recovery Services to recover data since the data may be spread across different parts of the SSD. Recovery from an SSD, especially after TRIM has been executed, may not always be possible, and even when it is, it often requires highly specialized tools and knowledge.
Physical Damage and Its Impact on Recovery
Physical damage is a significant concern for both HDDs and SSDs, but it has different implications for each. For HDDs, physical damage—such as a head crash or motor failure—can cause a complete loss of data, and repairing these drives usually requires replacing components inside a cleanroom environment. However, because HDDs store data magnetically on rotating platters, the data is often recoverable if the physical damage is addressed quickly and the drive is handled carefully.
For SSDs, physical damage is less common due to the lack of moving parts. However, issues such as power surges, faulty controllers, or physical damage to the NAND chips can still occur. Recovering data from an SSD with physical damage often requires specialized IT Service to address these issues, and the success rate of recovery can be lower compared to HDDs due to the complexity of the storage technology.
Logical Failures: How Data Recovery Works for Both Hard Drives and SSDs
When data loss occurs due to logical failure, it doesn’t necessarily mean the data is gone. Both HDDs and SSDs can suffer logical failures such as file corruption, accidental formatting, or partition loss. For HDDs, Data Recovery Services typically involve the use of software tools to scan the drive and restore lost files. This process can be relatively straightforward as long as the physical drive remains intact.
For SSDs, logical failures may not always be recoverable due to the limitations of TRIM and wear leveling. If a failure occurs, data recovery tools for SSDs attempt to access the data blocks where the files were stored, but due to the nature of how SSDs manage data, the recovery process may be much more complicated and less successful. In some cases, if data has been deleted or corrupted beyond repair, professional Data Recovery Customer Service might be able to offer partial recovery depending on the specific failure.
Cost of Data Recovery: Hard Drives vs. SSDs
The cost of recovering data from an HDD versus an SSD varies widely based on the complexity of the failure. Data Recovery Services for HDDs can range from relatively affordable services for logical failures to more expensive recovery for severe mechanical damage. The cost of recovering data from an SSD is generally higher due to the complexity of the recovery process, especially if the failure involves TRIM or wear leveling issues.
Data Recovery Services for SSDs can also take longer, especially when dealing with advanced technologies like NAND flash memory, and might require more specialized equipment. As SSD technology continues to evolve, so too does the need for advanced recovery techniques, which can increase the cost of recovery.
Success Rates in Data Recovery: HDD vs. SSD
The success rate for data recovery from HDDs and SSDs can vary depending on the type of failure. HDDs tend to have higher success rates for recovery, especially for logical failures. As long as the drive isn’t physically damaged beyond repair, there is a good chance that data can be recovered.
SSDs, however, have lower success rates in data recovery, particularly when TRIM has been executed or the wear leveling has overwritten the data. In cases of extreme failure or if data is permanently erased, recovery can be impossible. However, skilled Data Recovery Services professionals may still have tools and techniques that can provide a chance at recovery, although it is far from guaranteed.
Data Recovery Software: What Works Best for Hard Drives vs. SSDs?
When it comes to Data Recovery Services, software tools for HDDs and SSDs differ significantly. For HDDs, numerous software tools are available for recovering lost or deleted files, as long as the drive is not physically damaged. These tools can scan the drive for corrupt or missing files and offer an easy recovery process.
For SSDs, recovery software is more complex due to the unique characteristics of the drive, such as TRIM and wear leveling. Specialized tools are required to attempt recovery, and success can be limited. Many data recovery professionals use proprietary software that is designed specifically for SSDs, but the process is often more difficult and expensive.
When to Seek Professional Help for Data Recovery
If you are facing data loss from either an HDD or an SSD, seeking professional help is often the best course of action. While DIY recovery tools may be effective for simple data loss scenarios, professional Data Recovery Services have the expertise and specialized equipment to handle complex failures, especially those involving physical or logical damage. If you attempt to recover data yourself, you risk causing further damage to the device, making recovery impossible.
Conclusion
While both HDDs and SSDs serve as storage devices, the data recovery process for each is significantly different. HDDs offer a relatively straightforward recovery process, especially for logical failures, whereas SSDs present more challenges due to their use of TRIM and wear leveling. Understanding the specific recovery needs for each type of device can help guide you through the process of retrieving lost data. Whether dealing with physical damage or logical failures, seeking professional Data Recovery Services ensures the best chance of retrieving lost data, especially when dealing with more complex SSD recovery scenarios.
Category
Data Recovery
Previous Post
Why Is Data Recovery Important for Businesses and Individuals?
In today’s fast-paced, data-driven world, losing access to your information can bring business...
Next Post
What Is the Success Rate of Professional Data Recovery?
Data loss is an unavoidable reality, whether caused by hardware failure, accidental deletion, or sys...
Today's businesses span borders, requiring versatile solutions.

 Admin
Admin
